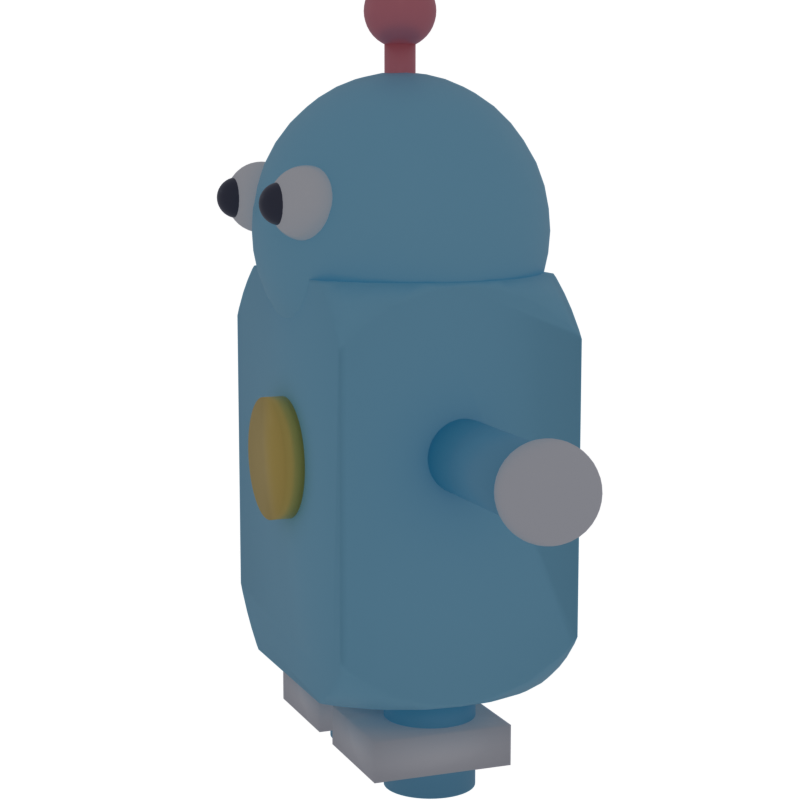
Parametric CAD in Rust. Define parts with CSG operations and export to STL, glTF, USD, and DXF.
Built on manifold for boolean operations and mesh generation.
use vcad::{centered_cube, centered_cylinder, Part};
// Plate with four mounting holes
let plate = centered_cube("plate", 100.0, 60.0, 5.0);
let hole = centered_cylinder("hole", 3.0, 10.0, 32);
let holes = hole.linear_pattern(80.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2)
.linear_pattern(0.0, 40.0, 0.0, 2)
.translate(-40.0, -20.0, 0.0);
let part = plate - holes; // operator overloads for CSG
part.write_stl("plate.stl").unwrap();Primitives — cube, cylinder, cone, sphere, centered variants
CSG — union (+), difference (-), intersection (&), plus named methods
Transforms — translate, rotate, scale, mirror, linear/circular pattern
Inspection — volume, surface area, bounding box, center of mass, triangle count
Export formats:
| Format | Use case | Feature flag |
|---|---|---|
| STL | 3D printing, CNC | always on |
| glTF/GLB | Web viewers, PBR materials | gltf (default) |
| USD/USDA | Isaac Sim, Omniverse | usd |
| DXF | Laser cutting (2D profiles) | always on |
| STEP | Interchange (requires OCCT) | step |
Materials — PBR material database loaded from TOML, with part-to-material assignments.
Scenes — Multi-part assemblies that preserve per-part materials for rendering.
If you've used OpenSCAD, CadQuery, or build123d:
- Rust-native. Your models are real Rust — cargo, crates, tests, CI. No custom language, no Python runtime.
- Watertight meshes. Built on Manifold. Every boolean op produces valid 2-manifold geometry. No mesh healing.
- Multi-format from one model. STL, glTF, USD, DXF, STEP — no conversion pipeline.
- Materials and scenes. PBR materials from TOML, multi-material GLB export for web viewers or Blender.
- Agent-friendly. Minimal API, operator overloads, consistent patterns. AI agents generate and iterate on models from natural language.
[dependencies]
vcad = "0.1"Without glTF support:
[dependencies]
vcad = { version = "0.1", default-features = false }use vcad::{centered_cube, centered_cylinder, Part};
let block = centered_cube("block", 30.0, 30.0, 20.0);
let bore = centered_cylinder("bore", 10.0, 25.0, 64);
let result = block.difference(&bore);use vcad::{centered_cube, bolt_pattern};
let flange = centered_cube("flange", 80.0, 80.0, 6.0);
let holes = bolt_pattern(6, 60.0, 5.5, 10.0, 32);
let part = flange.difference(&holes);use vcad::{Part, Scene};
use vcad::export::{Materials, export_scene_glb};
let materials = Materials::parse(r#"
[materials.steel]
color = [0.7, 0.7, 0.72]
metallic = 0.9
roughness = 0.4
[materials.rubber]
color = [0.1, 0.1, 0.1]
metallic = 0.0
roughness = 0.9
"#).unwrap();
let mut scene = Scene::new("assembly");
scene.add(Part::cube("frame", 100.0, 50.0, 30.0), "steel");
scene.add(
Part::cylinder("wheel", 20.0, 10.0, 32).translate(60.0, 0.0, 0.0),
"rubber",
);
export_scene_glb(&scene, &materials, "assembly.glb").unwrap();use vcad::export::DxfDocument;
let mut doc = DxfDocument::new();
doc.add_rectangle(100.0, 60.0, 0.0, 0.0); // outer profile
doc.add_circle(0.0, 0.0, 15.0); // center hole
doc.add_circle(-35.0, 0.0, 3.0); // mounting hole
doc.add_circle(35.0, 0.0, 3.0); // mounting hole
doc.add_bend_line(-50.0, 20.0, 50.0, 20.0); // bend (BEND layer)
doc.export("bracket.dxf").unwrap();# materials.toml
[materials.aluminum_6061]
color = [0.85, 0.85, 0.88]
metallic = 0.95
roughness = 0.35
density = 2700
description = "6061-T6 Aluminum"
[materials.abs_black]
color = [0.08, 0.08, 0.08]
metallic = 0.0
roughness = 0.7
density = 1040
[part_materials]
frame = "aluminum_6061"
cover = "abs_black"use vcad::export::Materials;
let mats = Materials::load("materials.toml").unwrap();
let frame_mat = mats.get_for_part("frame").unwrap();
assert_eq!(frame_mat.name, "aluminum_6061");| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
Part::cube(name, x, y, z) |
Box with corner at origin |
Part::cylinder(name, r, h, segments) |
Cylinder along Z |
Part::cone(name, r_bot, r_top, h, segments) |
Tapered cylinder |
Part::sphere(name, r, segments) |
Sphere at origin |
Part::empty(name) |
Empty geometry (identity for union) |
centered_cube(name, x, y, z) |
Box centered at origin |
centered_cylinder(name, r, h, segments) |
Cylinder centered at origin |
counterbore_hole(d, cb_d, cb_depth, depth, seg) |
Through hole + counterbore |
bolt_pattern(n, bcd, hole_d, depth, seg) |
Circle of holes |
| Method / Operator | Description |
|---|---|
a.union(&b) or a + b |
Boolean union |
a.difference(&b) or a - b |
Boolean difference |
a.intersection(&b) or a & b |
Boolean intersection |
All operators work on both Part and &Part.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
.translate(x, y, z) |
Move |
.translate_vec(v) |
Move by nalgebra Vector3 |
.rotate(x_deg, y_deg, z_deg) |
Rotate (degrees) |
.scale(x, y, z) |
Non-uniform scale |
.scale_uniform(s) |
Uniform scale |
.mirror_x() / .mirror_y() / .mirror_z() |
Mirror across plane |
.linear_pattern(dx, dy, dz, count) |
N copies along vector |
.circular_pattern(radius, count) |
N copies around Z axis |
| Method | Returns |
|---|---|
.volume() |
f64 — mesh volume |
.surface_area() |
f64 — total surface area |
.bounding_box() |
([f64; 3], [f64; 3]) — AABB min/max |
.center_of_mass() |
[f64; 3] — volume-weighted centroid |
.num_triangles() |
usize — triangle count |
.is_empty() |
bool — has geometry? |
| Method / Function | Format |
|---|---|
part.write_stl(path) |
Binary STL file |
part.to_stl() |
Binary STL bytes |
export_glb(part, material, path) |
glTF binary (single part) |
export_scene_glb(scene, materials, path) |
glTF binary (multi-material) |
export_usd(part, material, path) |
USD with physics |
export_robot_usd(body, wheels, ...) |
USD articulated robot |
DxfDocument::new() + .export(path) |
DXF R12 for laser cutting |
let plate = centered_cube("plate", 120.0, 80.0, 4.0);
let holes = centered_cylinder("hole", 2.5, 10.0, 32)
.linear_pattern(100.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2)
.linear_pattern(0.0, 60.0, 0.0, 2)
.translate(-50.0, -30.0, 0.0);
let part = plate - holes;let arm = centered_cube("arm", 40.0, 10.0, 5.0).translate(25.0, 0.0, 0.0);
let bracket = &arm + &arm.mirror_x(); // symmetric about YZ planelet hub = centered_cylinder("hub", 15.0, 20.0, 64);
let flange = centered_cylinder("flange", 30.0, 4.0, 64).translate(0.0, 0.0, -10.0);
let bore = centered_cylinder("bore", 5.0, 25.0, 32);
let bolt_holes = bolt_pattern(6, 45.0, 3.0, 8.0, 32).translate(0.0, 0.0, -10.0);
let part = hub + flange - bore - bolt_holes;let wall = 2.0;
let outer = centered_cube("outer", 60.0, 40.0, 30.0);
let inner = centered_cube("inner", 60.0 - wall * 2.0, 40.0 - wall * 2.0, 30.0 - wall)
.translate(0.0, 0.0, wall);
let box_part = outer - inner;
let lid = centered_cube("lid", 60.0, 40.0, 3.0).translate(0.0, 0.0, 30.0);let slot = centered_cube("slot", 15.0, 2.0, 10.0);
let vents = slot.circular_pattern(20.0, 8);
let panel = centered_cylinder("panel", 35.0, 3.0, 64) - vents;vcad pairs well with the Blender MCP server for AI-assisted 3D workflows. Export a GLB from vcad, then import and preview it in Blender — all from a single conversation with an AI agent.
// Generate and export
let plate = centered_cube("plate", 100.0, 60.0, 5.0);
let holes = bolt_pattern(4, 80.0, 6.0, 10.0, 32);
let part = plate - holes;
part.write_stl("plate.stl").unwrap();
// Export multi-material scene as GLB
export_scene_glb(&scene, &materials, "assembly.glb").unwrap();Then in Blender (via MCP):
# Import the GLB into the current scene
bpy.ops.import_scene.gltf(filepath="assembly.glb")The MCP server exposes tools for scene inspection, viewport screenshots, and Python execution — so an AI agent can generate geometry with vcad, import it into Blender, position cameras, and render previews in a single loop.
vcad is unit-agnostic — coordinates are just f64. By convention, the projects using vcad treat values as millimeters (matching STL/DXF conventions for manufacturing).