This repository contains the Docker Compose file and configuration for setting up a QGIS Stack. It includes services for PostgreSQL with PostGIS, Syncthing, PgAdmin, and Caddy.
- Docker and Docker Compose How to install for Linux and macOS and Windows
- Make (
sudo apt install make) for linux - if you are windows you can run it with run.bat file
The project uses the following environment variables, which are set in the .env file:
COMPOSE_PROJECT_NAME=qgisPOSTGIS_VERSION_TAG=15-3.3POSTGRES_PORT=5432POSTGRES_USER=postgresPOSTGRES_PASSWORD=graficaALLOW_IP_RANGE=0.0.0.0/0PGADMIN_VERSION_TAG=7.0PGADMIN_PORT=8085PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL=gmioannou@gmail.comPGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD=grafica
By default, the provided configuration in this repository uses placeholder domain names. To change the domain names and use Let's Encrypt staging for the staging environment, follow the steps below:
-
Configure the DNS settings for your domain names:
-
If you already own the domain names you specified in the Caddyfile, make sure to set up A records pointing to the IP address of the server where you will be hosting your services. You can usually do this through your domain registrar's control panel or DNS management interface.
-
If you are testing locally or in a development environment, you can modify your local hosts file (
/etc/hostson Unix-like systems orC:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hostson Windows) to map the domain names to the IP address of your local machine.
-
-
Open the
./caddy/Caddyfilein a text editor.
Proper DNS configuration is essential to ensure that the domain names resolve to the correct IP address when accessed from a web browser.
-
Replace all occurrences of
example.comwith your desired domain name for each service. For example, replacesyncthing.example.com,pgadmin4.example.com, andapi.example.comwith the respective domain names you want to use. -
To use Let's Encrypt staging for the staging environment, add the following line at the top of your
Caddyfileor remove it in production:{ acme_ca https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory } -
The
Makefileprovides commands for interacting with the stack:
make up: Starts the stack using Docker Compose.make copy-demo: Copies the content of theSyncdirectory to thesyncthingservice.make down: Stops the stack using Docker Compose.
NOTE: Any new edits on Caddyfile you will need to restart the Caddy server (container) to apply the new configuration.
This tutorial guides you through setting up Syncthing to synchronize files between two devices, referred to as the "local device" and the "remote device." It's recommended to install and configure Syncthing on both devices simultaneously, but it's okay if you can't access both at the same time.
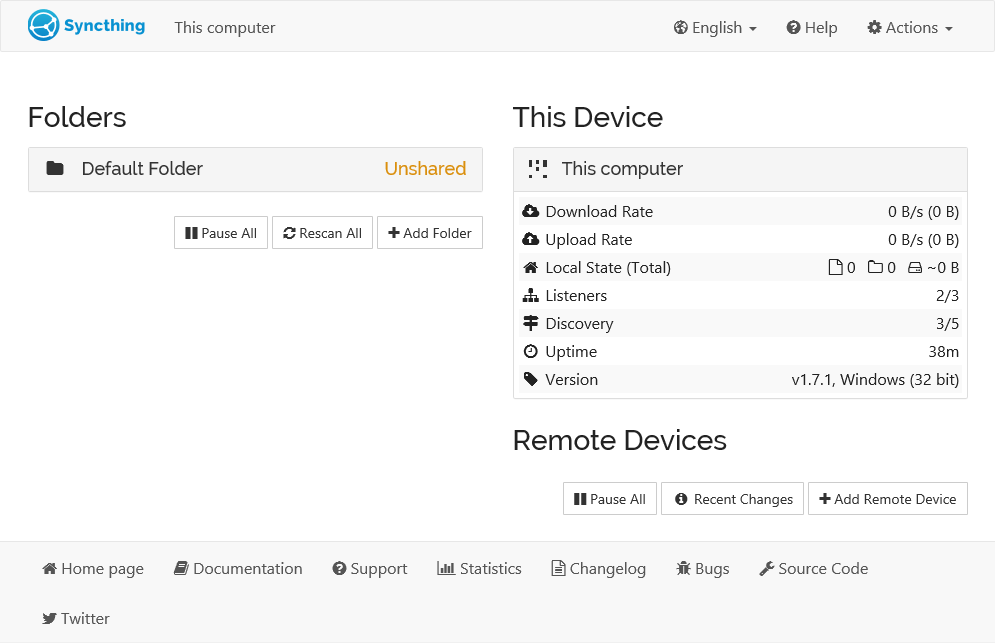
- Syncthing sets up a folder called
Default Folderin a directory namedSyncin your home directory upon the first start. - The admin GUI is available at
https://syncthing.example.com/. On the left is a list of folders (directories to synchronize), and on the right is a list of devices. TheDefault Folderis marked as "Unshared" initially because it's not shared with any other device.
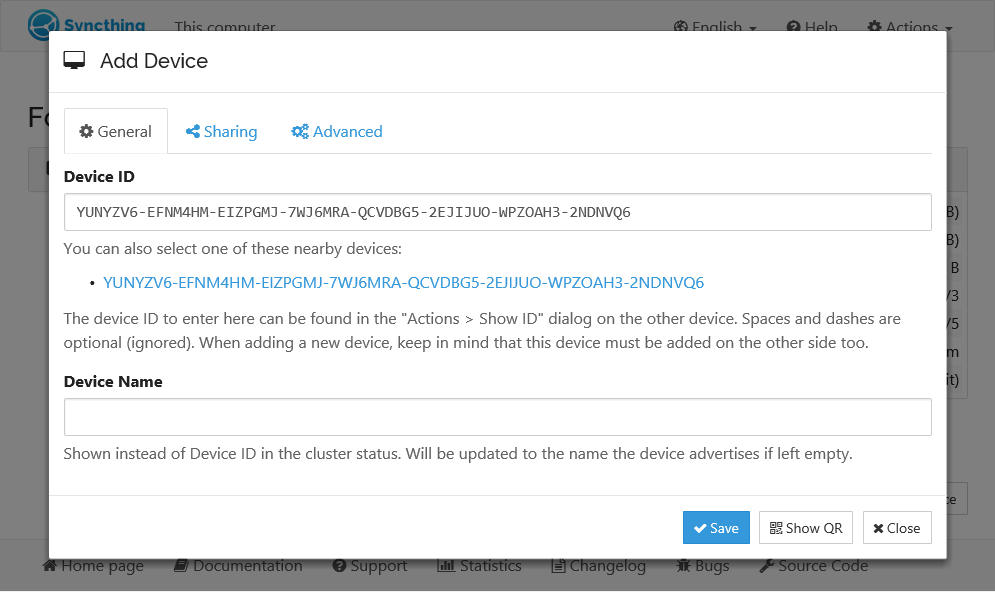
- To synchronize files with another device, exchange "device IDs." A device ID is a unique identifier generated when you first start Syncthing. Find it in the web GUI under "Actions" > "Show ID".
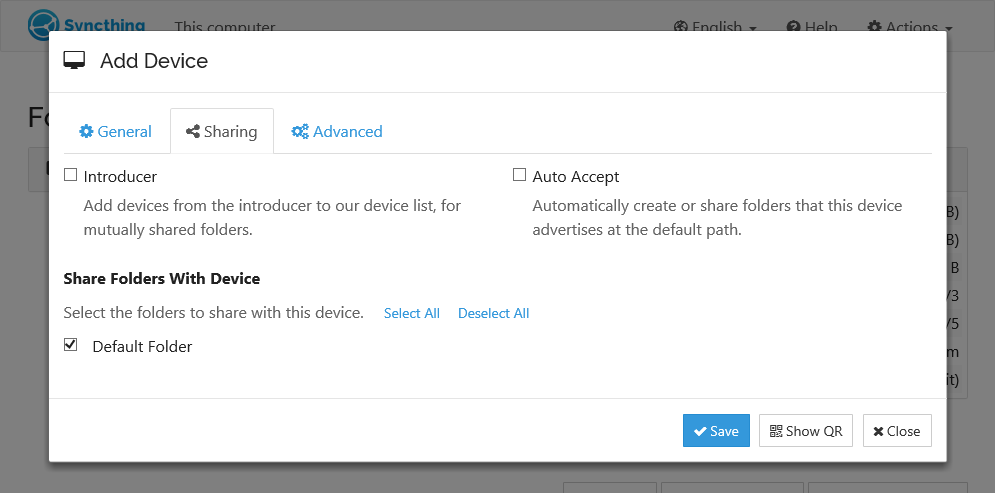
- Click "Add Remote Device" and enter the other device's ID. Also, select the folder(s) you want to share. The device name is optional.
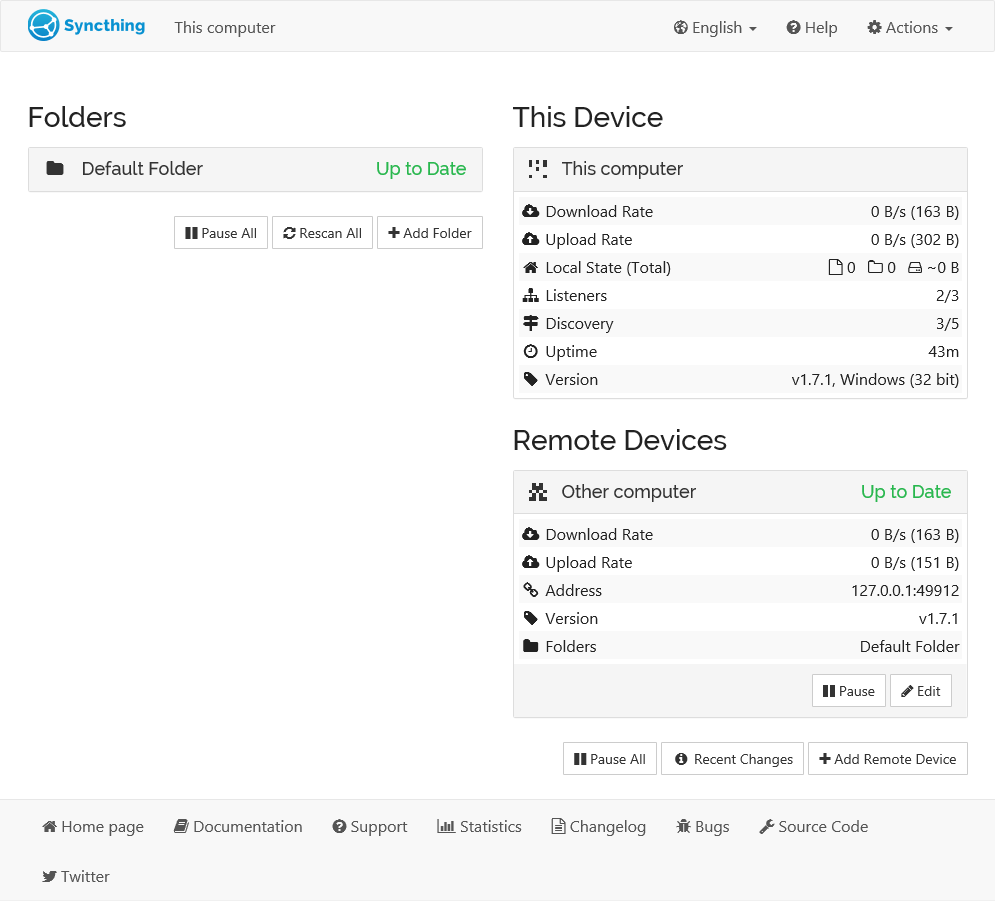
- After clicking "Save," the new device will appear on the right side of the GUI. It will connect within a minute or so. Now, adding files to the shared directory on either device will synchronize those files to the other side.
For additional support, refer to the Community Contributions page.
Contributions are welcome! Please submit a pull request or open an issue to discuss your proposed changes.
This project is open source and available under the MIT License.